Adenoidectomy
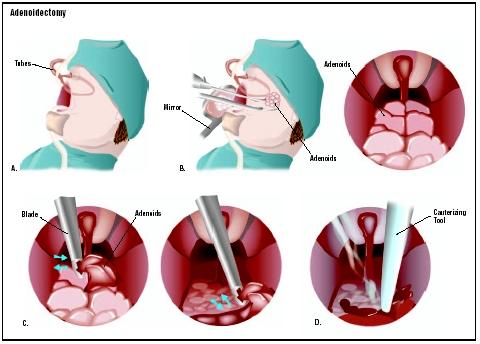
What is Adenoidectomy
An adenoidectomy, or adenoid removal, is surgery to remove the adenoid glands.
While adenoids help protect the body from viruses and bacteria, they sometimes become swollen and enlarged or chronically infected. This can be due to infections, allergies, or other reasons. Some children may also be born with abnormally large adenoids.
When a child’s adenoids become enlarged, they can cause problems by partially blocking his or her airway. When this happens, children can have breathing problems, ear infections, or other complications, which can lead to snoring or more serious conditions such as sleep apnea (stopping breathing) at night.
Chronic (long-term) nasal drainage, congestion and sinus infections can also be seen. Enlarged adenoids can also affect the recurrence (return) of ear infections and chronic fluid in the ear, which can result in temporary hearing loss.
Surgery to remove the glands is often needed. Removing them has not been shown to affect a child’s ability to fight infections.
An adenoidectomy is mostly done for children who are between the ages of 1 and 7. By the time a child is 7, the adenoids begin to shrink, and they are considered a vestigial organ in adults (a remnant with no purpose).
Tonsillectomy
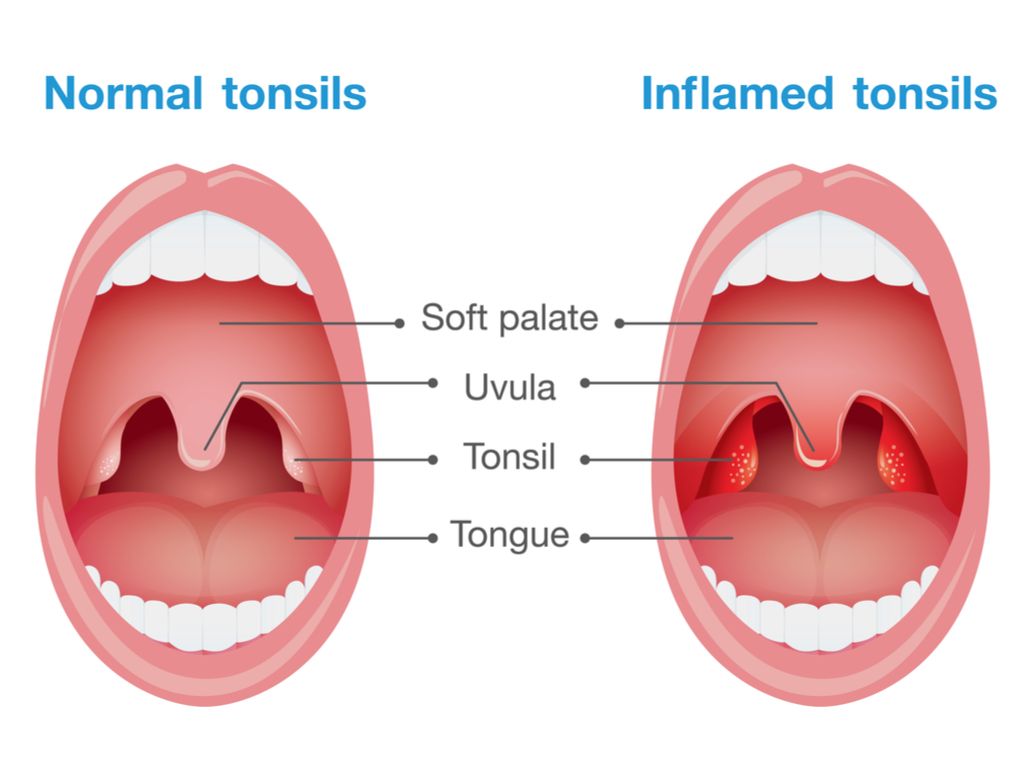
What is Tonsillectomy
A tonsillectomy is an operation to remove the tonsils from the back of the throat.In some cases the adenoids are also removed, in which case the operation is known as an adeno-tonsillectomy. Adenoids are made of similar tissue to tonsils and hang from the back of the nose, above your throat, where you cannot see them. They are also part of the immune system. They shrink on their own in childhood once they are no longer needed.
Tonsillectomy is an operation most often done in childhood; however, it can be done in adults as well. It is a common procedure.
What are the benefits of having a tonsillectomy?
Tonsils are usually removed because they are causing problems. Common reasons for taking tonsils out are:
- Repeated (recurring) attacks of infection of the tonsils (tonsillitis). If you have bouts of tonsillitis which are frequent or severe, having your tonsils removed stops this happening. However, it does not stop you having sore throats and other throat infections.
- Recurring abscesses around the tonsil (called quinsy).Tonsils (and/or adenoids) are getting in the way of the airway, making it difficult to breathe, sleep or eat. For example if you have a condition called obstructive sleep apnoea, removing tonsils and adenoids may be helpful.
- Ulcer or Growths on the tonsil that need further investigation (Biopsy).
Peritonsillar Abscess Drainage GA
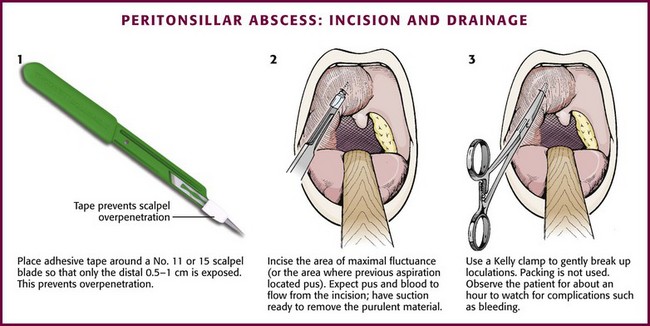
What is Peritonsillar Abscess Drainage GA
Classic clinical signs and symptoms of peritonsillar abscess (PTA), also known as quinsy, include fever, sore throat, muffled voice, odynophagia, asymmetry of tonsils, swelling of soft palate, and deviation of uvula. Some patients complain of ipsilateral otalgia. Bilateral PTA can present with significant trismus and can be very difficult to diagnose on clinical grounds alone.
Young children with deep neck space abscesses tend to have a more subtle presentation. They are seldom able to verbalize their symptoms or cooperate with the physical examination. Their oropharynx is frequently difficult to examine because of its small size.
Patients younger than 4 years old present more frequently with agitation, cough, drooling, lethargy, respiratory distress, rhinorrhea, and stridor and less frequently with positive physical signs on oropharyngeal examination and trismus compared with patients 4 years or older.
Physical examination can be difficult in patients with trismus or respiratory distress. Aggressive physical examination should be avoided in these cases in order to prevent catastrophic respiratory failure due to a spontaneous abscess rupture or epiglotitis. Instead, imaging (computed tomography [CT] or intraoral ultrasound) or exam by a skilled otolaryngologist under controlled conditions, with artificial airways in place will confirm the diagnosis.
Tracheostomy
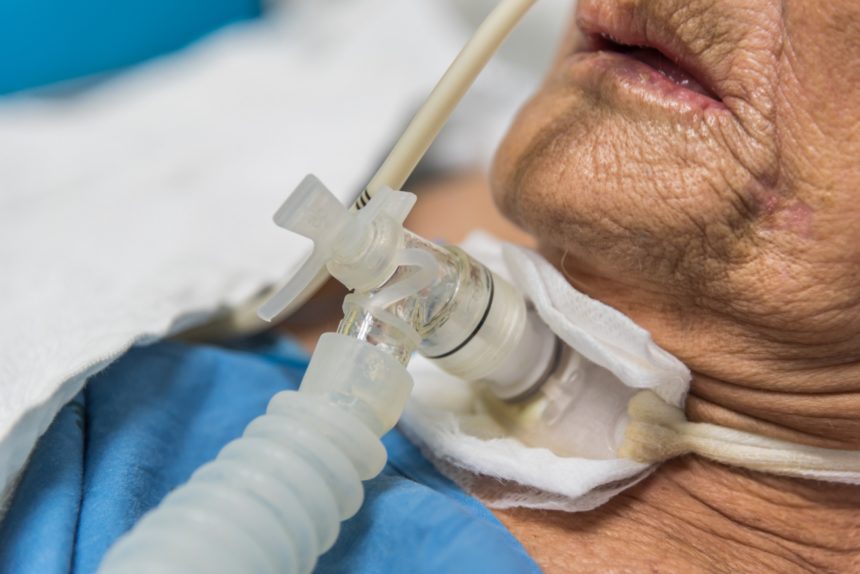
What is Tracheostomy
Tracheostomy (tray-key-OS-tuh-me) is a hole that surgeons make through the front of the neck and into the windpipe (trachea). A tracheostomy tube is placed into the hole to keep it open for breathing. The term for the surgical procedure to create this opening is tracheotomy.
A tracheostomy provides an air passage to help you breathe when the usual route for breathing is somehow blocked or reduced. A tracheostomy is often needed when health problems require long-term use of a machine (ventilator) to help you breathe. In rare cases, an emergency tracheotomy is performed when the airway is suddenly blocked, such as after a traumatic injury to the face or neck.
When a tracheostomy is no longer needed, it's allowed to heal shut or is surgically closed. For some people, a tracheostomy is permanent
Microlaryngeal Surgery (Vocal Cord Cyst / Polyp Removal)
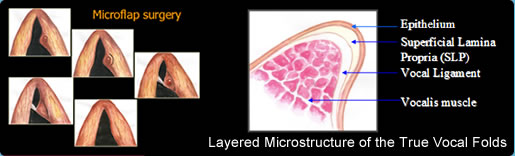
What is Microlaryngeal Surgery (Vocal Cord Cyst / Polyp Removal)
Treatment options for vocal fold nodules (VFNs) and vocal fold polyps (VFPs) include invasive and noninvasive techniques. [4] Prevailing thought reflects the opinion that the etiologic mechanisms of both lesions are most directly related to vocal use and technique. Therefore, attention to correcting the underlying causative factors, largely through voice therapy and education, plays an integral role in any treatment plan of action.
Education regarding proper vocal hygiene and hydration and avoidance of vocal abuse, misuse, and overuse is a necessary baseline. [19] The patient must comprehend how specific behaviors or patterns thereof may have contributed or may in the future contribute to vocal fold lesions
Voice Change Surgery
What is Microlaryngeal Surgery (Vocal Cord Cyst / Polyp Removal)
Voice feminizing therapy involves treatments to help transgender women (male to female) adapt their voices, resulting in communication patterns that match their gender identity. Treatments can help you change vocal characteristics, such as pitch and intonation, and nonverbal communication patterns, such as gestures and facial expressions. Surgery to raise your pitch also might be an option.
The way people speak, including their style, voice and choice of words, is highly personal. You'll choose which communication behaviors you want to acquire in agreement with your gender identity. Voice therapy shouldn't counsel you to adopt behaviors that aren't right for you. Also, keep in mind that changing your voice can take years and these changes can feel uncomfortable or inauthentic at first.
Voice feminizing therapy treatments depend on your needs. A specialist can help you determine your goals and create an individualized therapy plan, as well as show you how to prevent vocal damage as you change your voice.
Facial Fracture Repair (Maxilla / Frontal / Mandible / Nasal Bone Fracture)
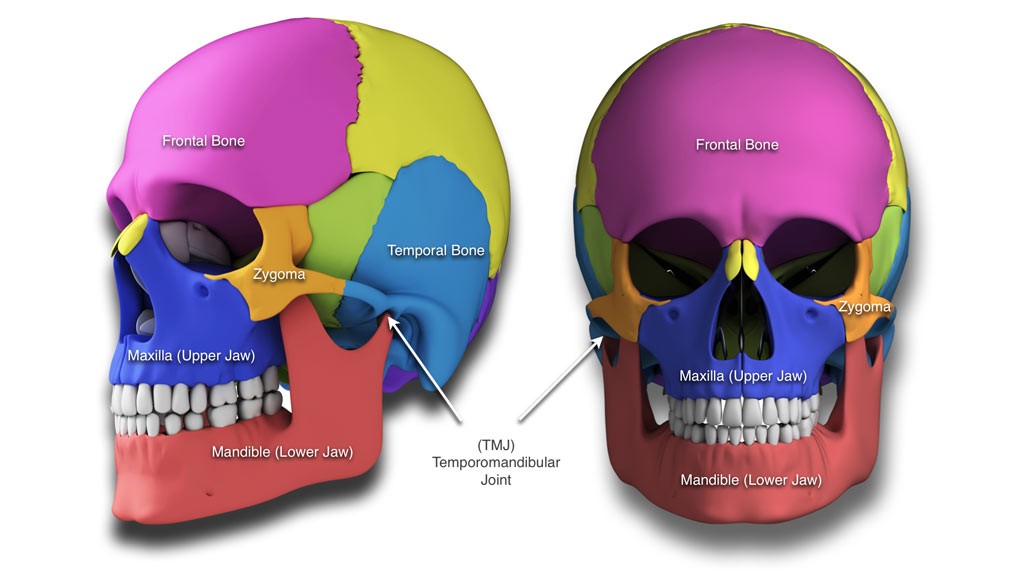
What is Facial Fracture Repair (Maxilla / Frontal / Mandible / Nasal Bone Fracture)
Nasal fractures are the most frequent isolated facial fractures in any facial fracture. Isolated nasal fractures are principally diagnosed through history and clinical examination. Closed reduction is the most frequently performed treatment for isolated nasal fractures, with a fractured nasal septum as a predictor of failure. Ear, nose, and throat surgeons develop an adequate treatment plan for patients with complex maxillofacial trauma.
